🆚 URL vs. Domain
Let’s be honest—most people use the terms URL and domain like they’re the same thing. I get it. Even in my early years as a web developer, I used to blur the two constantly. But once I started managing websites, running SEO audits, and working with clients on cybersecurity, I realized something important:
Knowing the difference between a URL and a domain can actually save you from tech headaches—and help you make smarter decisions online.
Whether you’re a casual browser or building your own website, this quick guide will help you finally understand what sets a URL apart from a domain—and why it matters more than you might think.
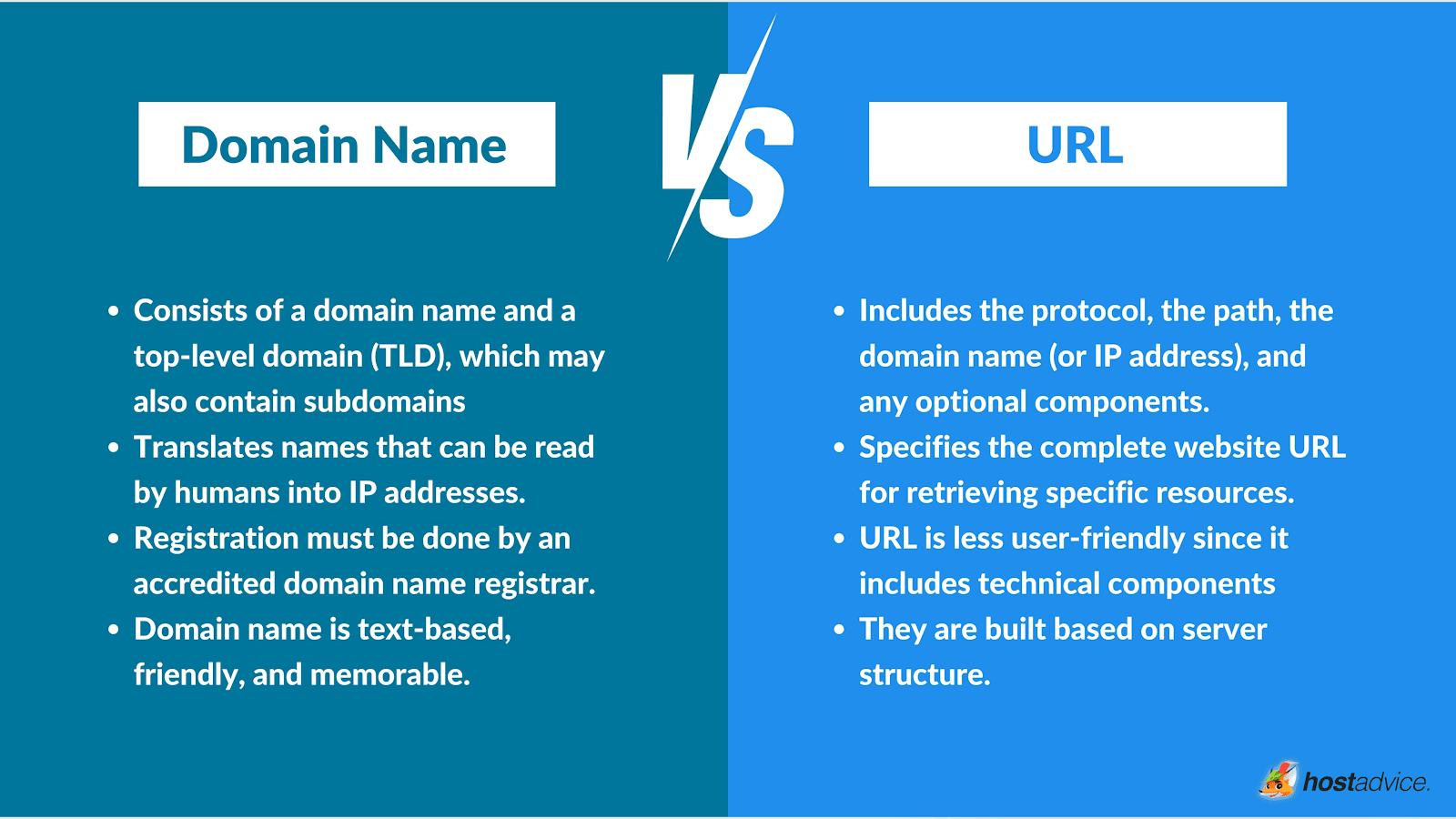
🧠 What Is a Domain?
Let’s start with the basics. A domain name is the main address of a website. It’s what you type into your browser when you want to visit a specific site, like:
Technically, a domain is your shortcut to an IP address (a string of numbers the internet uses to locate a server). Instead of typing something like 142.250.190.14, you just type google.com—much easier, right?
🔁 Real-Life Analogy
Think of a domain like your home address. It tells people where to find your house on the map, but it doesn’t say what room you’re in or what you’re doing.

🔎 What Is a URL?
Now let’s take it a step further. URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It’s the full web address that includes the domain plus extra information, such as:
The protocol (HTTP or HTTPS)
The specific file path or page
Any parameters, anchors, or query strings
Here’s an example:
👉 https://www.nasa.gov/news/media-resources/?ref=homepage#gallery
This is a URL. It includes:
https→ the protocolwww.nasa.gov→ the domain/news/media-resources/→ the path to a specific section?ref=homepage→ a query parameter#gallery→ an anchor to a section on the page
🏠 Real-Life Analogy
If your domain is your street address, the URL is like a full set of directions telling someone how to get to your kitchen, what to bring, and where to hang their coat once they’re inside.
🔄 Key Differences Between a Domain and a URL
| Feature | Domain Example | URL Example |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Format | example.com | https://example.com/products/item?ref=summer-sale#top |
| Includes Path? | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Used in Linking? | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Length | Shorter | Longer, more descriptive |
| SEO Role | Branding & authority | Crawling, indexing, content structure |
💡 Why This Difference Matters
You might be thinking: “Okay, I get it… but why should I care?”
Let me explain.
🔐 For Casual Internet Users
If you’ve ever clicked a shady link in an email or on social media, you know how sketchy things can get. One of the easiest ways to spot a scam is to look closely at the full URL—not just the domain.
Example:
A scam site might show a link like secure.paypa1.com/verify-account (with a fake “1” instead of “l”), but the actual domain may be something like hacker-site.ru.
Knowing the difference can keep you from falling for phishing attempts.
📈 For Website Owners & Marketers
This is where things really get interesting.
Your domain builds trust—it’s your brand’s digital identity. But your URL structure affects SEO, usability, and click-through rates.
For instance:
A clean, readable URL like
example.com/shop/shoes/nike-air-maxis great for SEO.A messy one like
example.com/x12/hp/pageid=23984.php?dsku=9121? Not so much.
In my own experience managing SEO for small businesses, tweaking URLs to be more keyword-friendly resulted in higher rankings and more clicks. It’s a simple fix that many overlook.
🚫 Common Misconceptions About URLs and Domains
Let’s clear up a few common myths:
❌ “A URL is just a domain with HTTPS.”
Nope. A URL includes the full path, not just the protocol and domain.
❌ “They both go to the same place, so who cares?”
That’s like saying “123 Main St” and “123 Main St, Apt 5B” are the same address. They’re not.
❌ “As long as the page loads, the link must be safe.”
Not true. Malicious actors often hide malware in long, confusing URLs that look normal at a glance.
✅ Quick Tips to Spot the Difference (And Use It Wisely)
Check the address bar: The domain will be between
https://and the first/.Use hover preview: On desktops, hover over links to view the full URL before clicking.
For SEO: Keep your URLs short, readable, and keyword-rich.
For security: If the domain doesn’t match the expected brand (e.g.,
paypal.com), don’t click.
🧭 Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between a domain and a URL isn’t just technical trivia—it’s practical knowledge that helps you navigate the internet smarter, protect yourself from scams, and optimize your own web presence.
To recap:
A domain is the base address—your website’s name.
A URL is the complete web address that points to a specific page, file, or resource.
So next time someone throws around the term “URL,” you’ll know exactly what they mean—and why it’s worth paying attention.